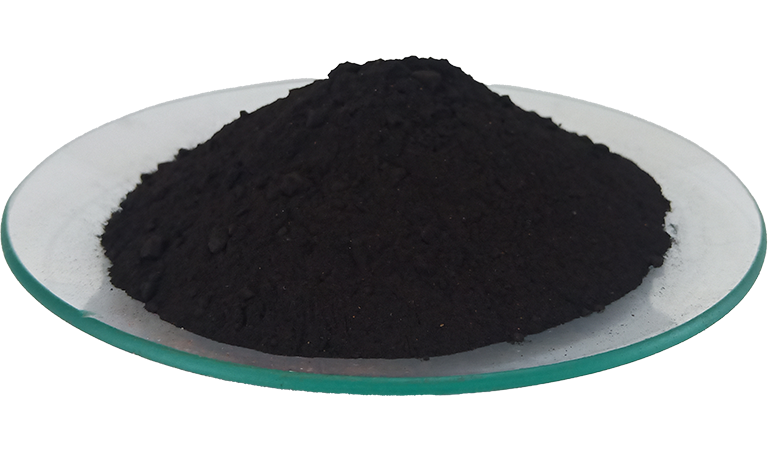
Copper Oxide

Product Introduction

Copper oxide (chemical formula: CuO) is an important inorganic compound playing a critical role in various industries such as electronics, chemicals, and industrial manufacturing. In the electronics sector, high-purity electronic grade copper oxide is extensively used for semiconductor materials. As a significant chemical raw material, copper oxide is applied in catalysts, battery materials, optical coatings, and more. In the glass and ceramics industry, it is used as a coloring agent, imparting unique blue-green hues to products. Additionally, in fireworks technology, copper oxide acts not only as a coloring agent but also as a catalyst, aiding in producing vibrant colors and stable combustion effects.
Specifications
Copper Oxide Content |
>97% |
Insoluble Impurities |
<0.1% |
Total Metallic Impurities |
<0.1% |
Chloride Content |
<0.1% |
Particle Size |
Micron-sized Powder |
Hou Jan Copper Oxide Advantages:
- Purity: Processed using copper raw materials with 99.9% purity.
- Particle Size: Produced through wet processing, ensuring better uniformity in particle size.
- Forms: Available in spherical and dendritic forms for selection.
Particle size range and copper oxide purity can be customized based on customer requirements.
Packaging Specifications
Our Copper Oxide Powder offers a variety of flexible packaging options to meet the needs of different customers:
- 1 kg packaging: Suitable for laboratory and small-scale production, easy to store and use.
- 5 kg packaging: Ideal for medium-scale production, ensuring stable supply and convenience.
- 20 kg packaging: Suitable for large-scale industrial applications, reducing the frequency of package changes and improving production efficiency.
We are committed to providing high-quality, reliable, and flexible products, ensuring that every choice you make is the best one.
Properties and Applications
Physical Properties of Copper Oxide

Copper oxide (CuO) has several essential physical properties, making it widely used in industrial and scientific applications. Copper oxide is typically found in the form of micron-sized powder, enhancing its reactivity in various applications.
Summary of Physical Properties:
- Color: Black
- Density: 6.3 to 6.6 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 1026°C
- Form: Micron-sized powder
- Structure: Monoclinic crystal system
- Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in dilute acids, ammonium chloride, and potassium cyanide. Insoluble in ethanol.
Chemical Properties of Copper Oxide

Copper oxide (CuO) has numerous crucial chemical properties, making it widely used in industrial and scientific applications. Copper oxide can serve as a catalyst in various organic synthesis reactions, especially in oxidation and desulfurization reactions. Additionally, copper oxide reacts with carbon monoxide (CO) to produce metallic copper and carbon dioxide, widely used in gas analysis and organic compound determination.
The chemical stability and reactivity of copper oxide make it an indispensable material in many industrial processes. For example, in PCB and semiconductor electroplating processes, copper oxide serves as a copper concentration supplement, ensuring the stability and uniformity of the electroplating process. Copper oxide's chemical properties also make it an essential component in petroleum desulfurization agents and organic synthesis catalysts.
Summary of Chemical Properties:
- Catalyst: Participates in organic synthesis reactions
- Reaction Products: Metallic copper and carbon dioxide
- Applications: Gas analysis, organic compound determination, PCB, and semiconductor electroplating processes
The chemical stability and reactivity of copper oxide make it an indispensable material in many industrial processes.
Industrial Applications of Copper Oxide

Copper oxide (CuO) has extensive applications in various industries, especially in the electronics, chemical, and metal processing sectors. In the electronics industry, copper oxide is used to manufacture electronic components, circuit boards, and batteries due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it a vital electronic material.
Furthermore, copper oxide is used as a copper concentration supplement in semiconductor manufacturing, ensuring the uniformity and stability of the electroplating process. In the chemical industry, copper oxide is commonly used as a catalyst or intermediate, particularly in the manufacturing of dyes, pigments, and coatings. Copper oxide's catalytic performance makes it an indispensable component in chemical reactions.
In the metal processing industry, copper oxide is used for metal surface treatment, such as electroplating and chemical plating processes. It not only improves the quality of the metal surface but also enhances the durability and corrosion resistance of the metal. Additionally, copper oxide plays a crucial role in metal recycling, helping to recover valuable metal resources. The copper oxide SDS provides safety handling guidelines for these applications, ensuring safety during use.
Summary of Industrial Applications:
- Electronics Industry: Electronic components, circuit boards, and batteries
- Chemical Industry: Manufacturing of dyes, pigments, and coatings
- Metal Processing Industry: Electroplating and chemical plating processes
- Metal Recycling: Recovering valuable metal resources
Overall, copper oxide has wide-ranging and essential applications in the industry, making it an indispensable material in modern industrial processes.
Applications of Copper Oxide in Chemistry and Analysis

Copper oxide (CuO) has extensive applications in chemistry and analysis, particularly in catalysis and analytical determinations. Copper oxide can serve as an organic synthesis catalyst, participating in various chemical reactions, including oxidation and desulfurization reactions, which are crucial for synthesizing various organic compounds.
Additionally, copper oxide is used in analytical chemistry, such as a nitrogen determination reagent and an oxidizing agent. Its application in nitrogen analysis allows for the precise determination of nitrogen content in organic compounds. Copper oxide reacts with carbon monoxide (CO) to produce metallic copper and carbon dioxide, making it an essential material in gas analysis. Copper oxide also plays a critical role in determining the carbon content of organic compounds.
These chemical properties of copper oxide make it indispensable in laboratory research and demonstrate its unique value in industrial applications. Furthermore, copper oxide is used as a copper concentration supplement in PCB and semiconductor electroplating processes, ensuring the uniformity and stability of the electroplating process.
Summary of Applications in Chemistry and Analysis:
- Organic Synthesis Catalyst: Participates in oxidation and desulfurization reactions
- Analytical Chemistry: Nitrogen determination reagent and oxidizing agent
- Gas Analysis: Produces metallic copper and carbon dioxide
- PCB and Semiconductor Electroplating: Copper concentration supplement
These applications highlight the multifunctionality and significance of copper oxide in chemistry and analysis, making it an essential material in chemical research and industrial production.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What are the main applications of copper oxide in the electronics industry?
Copper oxide is primarily used in the electronics industry for manufacturing electronic components, circuit boards, and batteries. Due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, copper oxide demonstrates superior performance in these applications. Additionally, copper oxide is used as a copper concentration supplement in semiconductor manufacturing, ensuring the uniformity and stability of the electroplating process.
Question 2: How is the toxicity of copper oxide determined?
The toxicity of copper oxide is typically determined through animal experiments and cell tests. Researchers assess the acute and chronic toxicity of copper oxide on biological systems, observing its effects on cells and tissues. Additionally, the MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) of copper oxide provides detailed information about its toxicity, including safety handling and protective measures.
Question 3: What are the specific applications of copper oxide in the chemical industry?
Copper oxide has various specific applications in the chemical industry, including as a catalyst, intermediate, and desulfurization agent. It plays a vital role in manufacturing dyes, pigments, and coatings. Additionally, copper oxide is used in organic synthesis reactions, participating in oxidation and desulfurization reactions to improve reaction efficiency and product quality.
Question 4: What safety measures are needed during the preparation of copper oxide?
During the preparation of copper oxide, the following safety measures are necessary: wearing protective gloves and goggles to avoid direct contact with skin and eyes; operating in a well-ventilated environment to avoid inhaling dust; strictly controlling reaction conditions to prevent excessive reactions that may lead to dangers. These safety measures effectively protect the health and safety of operators.
Question 5: What role does copper oxide play in environmental protection?
Copper oxide plays a significant role in environmental protection, primarily in wastewater treatment and air pollution control. As a catalyst, copper oxide promotes the decomposition and transformation of harmful substances, reducing pollutant emissions. Additionally, copper oxide is used in industrial wastewater treatment to effectively remove heavy metals and organic pollutants from water, protecting the aquatic environment.
Safety Data Sheet
Quick Browse All Products
Professional Services
Resource Reuse
Recycling and reuse of waste liquid from printed circuit boards and metal surface treatment, achieving resource circulation and environmental protection.
Learn moreMetal Etchant
Ferric Chloride Solution
Ferric Chloride: An efficient agent for metal etching, water treatment, and various industrial applications.
Learn moreWater Treatment Agents
Ferric Chloride Solution
Ferric Chloride: An efficient agent for metal etching, water treatment, and various industrial applications.
Learn moreFerrous Chloride Solution
Ferrous Chloride: A high-efficiency reducing agent for wastewater treatment, fabric dyeing, and various industrial uses.
Learn morePoly Aluminum Chloride (PAC)
Poly Aluminum Chloride: An efficient wastewater treatment agent, suitable for various types of wastewater, improving treatment efficiency.
Learn moreCalcium Chloride
Calcium Chloride: Used for fluorine-containing wastewater treatment, refrigeration, ice making, and as an antifreeze in construction.
Learn moreDiverse Copper Metals
Copper Powder
Copper Powder: High purity, suitable for powder metallurgy, electronic components, and chemical catalysts.
Learn moreCopper Oxide Powder
Copper Oxide: Used in catalysts, glass coloring, analytical reagents, and petroleum desulfurization.
Learn moreCuprous Oxide Powder
Cuprous Oxide: Used in antifouling paint, pesticides, red glass, and copper salt production.
Learn moreSilver-Coated Copper Powder
Silver-Coated Copper Powder: Enhances conductivity and oxidation resistance, suitable for conductive adhesives, paints, and inks.
Learn more








